Staking Explained
To keep their networks secure, blockchains reward people with cryptocurrency. There are various consensus mechanisms enabled to validate transactions on the blockchain. For example, Bitcoin uses a Proof of Work mining algorithm, while NEM has introduced a Proof of Importance system.

One additional alternative used by cryptocurrencies, such as Dash, Polkadot, Neo and Cardano, is the Proof of Stake mechanism, which is considered an energy-saving method to confirm cryptocurrency transactions.
In today’s SpectroCoin blog post, we are happy to clear up the confusion around the concept of “Proof of Stake” and share our thoughts about staking.
What is staking?
In simple words, staking is the activity of locking a certain amount of cryptocurrency in the blockchain to receive rewards. When a participant (a node) locks (stakes) a cryptocurrency, they become eligible to vote in the transaction approval process. Usually, the process of voting is automatic and does not require any additional steps from a person.
To get a clearer idea of what staking is, it is crucial to understand how Proof of Stake works. As mentioned earlier, it is a consensus mechanism that cost-effectively maintains the level of decentralization.
In Proof of Stake mechanism, people can simply lock a certain amount of coins (a “stake”) and the person who validates a block is selected by the protocol. Usually, the higher amount of coins is set as stake, the more blocks the person will be able to validate. Thus, if you lock up a higher amount of cryptocurrency, you will have more opportunities to be designated to approve the block.
Each network takes into account different factors that determine staking rewards. These factors can be, for example, the number of coins put as a stake, the number of total coins staked in the network, the inflation rate, and the time frame in which a validator has been actively staking.
Alternatively, some networks set a fixed reward percentage and distribute it among validators to compensate for inflation. This model helps to calculate the expected staking reward and increases the usage of the cryptocurrency.
While networks pay for people to maintain security, it is essential to note that with Proof of Stake, the coins held as stakes motivate validators to keep the platform secure. Otherwise, their stake could be compromised.
Hence, staking can be considered as simply holding funds in a wallet. Because of this, almost anyone can contribute to the network functionality and receive rewards in return.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
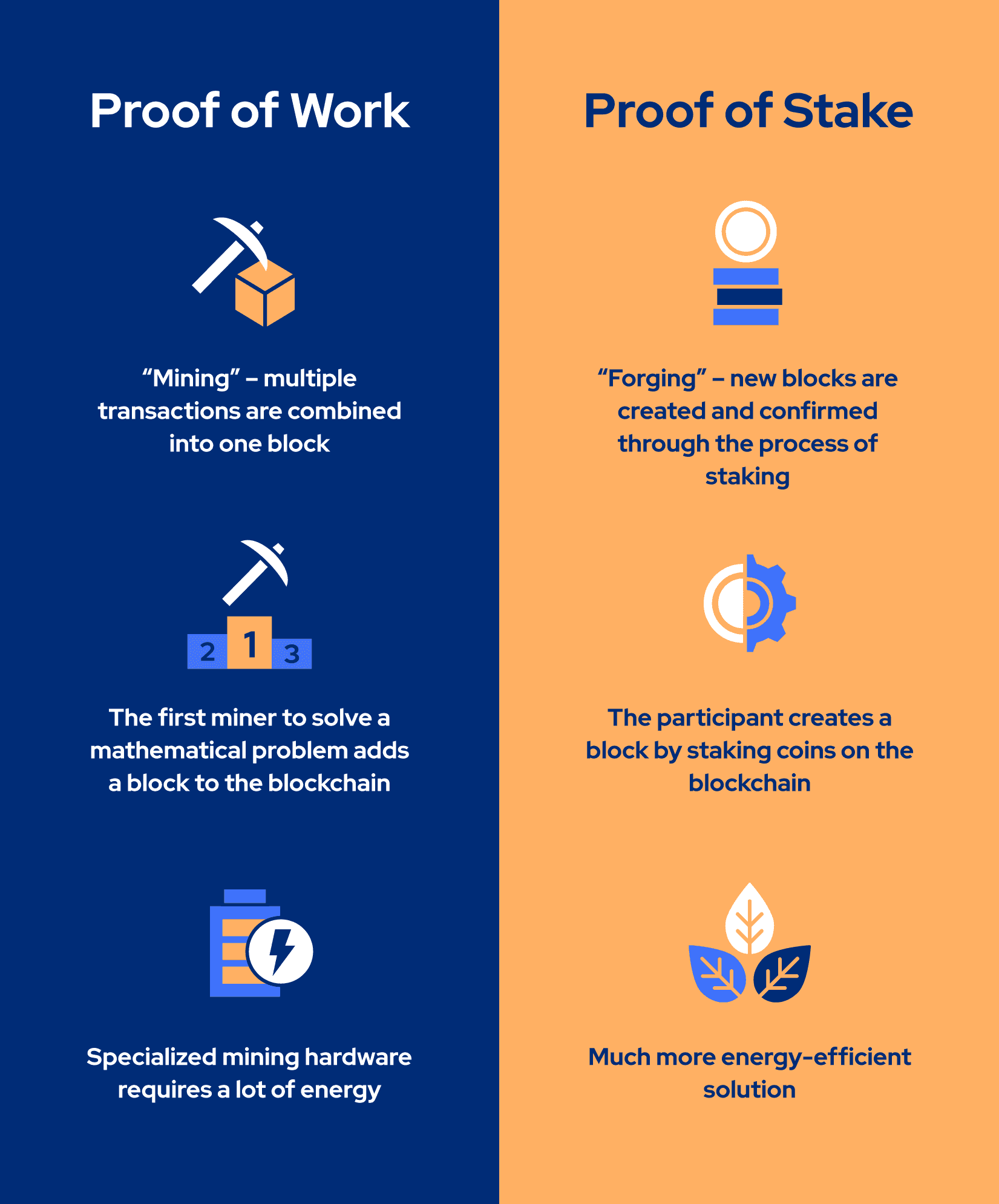
Although both mechanisms are used to validate transactions and keep the network secure, there are significant differences in their usage. The most popular cryptocurrency Bitcoin uses a Proof of Work mining algorithm that allows one party to prove to others that a certain amount of computer power was used to validate a transaction. This method, however, requires a lot of energy, which is harmful to the environment.
In the case of Bitcoin, the Proof of Work mechanism combines multiple transactions into one block. The blocks are merged into the blockchain. The first miner to solve a mathematical problem adds a block to the blockchain. In this way, miners compete to solve this puzzle, and such competition requires a lot of computer power.
On the other hand, staking requires fewer resources and can be considered as an energy-saving alternative to mining. In the case of Proof of Stake, creating new blocks is called “forging” rather than “mining”. Proof of Stake systems often use coins that have already been mined, or start with Proof of Work and later move to Proof of Stake.
As we explained before, in the Proof of Stake systems, instead of mining, new blocks are created and confirmed through the process of staking. This allows participants to produce new blocks without relying on specialized mining hardware. Instead, they only need to hold their cryptocurrency in a suitable wallet. Thus, Proof of Work does not complicate things to aspiring miners.
When it comes to the reward system, Proof of Work mechanisms generate more cryptocurrency to pay out to network participants. Conversely, transaction fees are used to reward people in Proof of Stake. So, the main idea of Proof of Stake lies in participants gaining the ability to create a block by having more staking coins, rather than competing to solve a hash challenge, as in Proof of Work.
Finally, the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism reduces the risk of attack on a blockchain network. Such attacks might take place if a person or a group gains control of more than 50% of the cryptocurrency and becomes eligible to make changes to a block (so-called “51% attack”). To achieve this in the Proof of Stake system, attackers would have to purchase the coins on the market. Hence, they would spend more than they could gain from the attack.
Why is staking beneficial?
Staking opens up new ways for crypto holders to participate in the blockchain consensus mechanisms. As the minimum amount to enter the system gets smaller, crypto holders can start validating transactions without putting a lot of effort into software setup and spending a fortune on electricity.
In this way, staking stimulates the inclusion of new members into the community of blockchain validators.
What do you think about staking? Share your comments on our social media channels, we are excited to hear them!