DeFi Explained
The idea of cryptocurrency lies in financing accessible to everyone, regardless of what part of the world they reside in. This is where DeFi, short for “decentralized finance”, steps in. Previously known as “open finance”, this movement aims to provide access to financial services like savings, loans, insurance, trading, and more – all with the help of blockchain technology.

Last week, we started the SpectroCoin blog series educating on various crypto topics. Today, we are excited to continue by sharing some insight into DeFi and take a closer look at the benefits and challenges that come together with the term.
What is DeFi?
Simply put, DeFi refers to a variety of cryptocurrency and blockchain applications designed to reduce financial intermediaries. Third parties might sometimes lead to a lack of speed and convenience in financial transactions, as well as people losing control of their funds. Thus, DeFi draws inspiration from blockchain technology, where anyone can own a copy of the transaction history, meaning it is not governed by a single source.
Moreover, DeFi extends the idea of blockchain by offering more complex financial service use cases. In addition to conducting a transaction without handing over control of your funds to a third party, DeFi takes a broader approach and aims to use loans, insurance, or exchanges as a means of decentralized finance.
The idea for the above complex applications was highlighted in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin, the creator of Ethereum. Today, most DeFi applications are based on the Ethereum blockchain. The reason for this is the functionality of smart contracts, which allows transactions to be executed when certain conditions are met, offering much more flexibility.
Various types of DeFi applications exist, the most popular being Decentralized Exchanges (DEX), stablecoins, lending platforms, and prediction markets. Let’s have a look at each of these applications.
Decentralized Exchanges
In most decentralized exchanges, it is not necessary to deposit or withdraw currency before the exchange. This means that no counterparty can gain possession of your funds at any point. Instead, you have full control over your money.
There are different types of DEXs, namely those where transactions are executed on-chain, off-chain order books, and automated market makers. While all of these categories fall under the concept of DEX, they share some significant differences.
On-chain transactions require all network participants (so-called “nodes”) to record each order on the blockchain. Because of this, one must pay a fee and wait while miners add the transaction to the blockchain. The examples of off-chain order books are Stellar and Bitshares DEXs.
In contrast, the records in off-chain books are organized in a centralized entity. For instance, ERC20 and other tokens built on the Ethereum blockchain provide a structure for parties known as “relayers” to manage off-chain books. In this way, relayers execute orders when the parties match.
Finally, automated market makers (AMMs) do not involve order books but use smart contracts to create liquidity pools (crypto assets held to facilitate trading pairs on decentralized exchanges) to execute transactions when specific parameters are met automatically. Popular DEX platforms that use AMM include Uniswap and Kyber Network.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies backed by a fiat currency, usually the US dollar. In the context of DeFi, stablecoins are not directly pegged to a fiat currency, meaning that they are not linked to a central authority in any way.
As an example, DAI is backed by cryptocurrency collateral and is over-collateralized. If you lock a $1 value of Ethereum, you are able to borrow a $0.66 cent value of DAI. To unlock Ethers, one would only need to pay back DAI. If you do not have Ethers, you can buy DAI in an exchange.
Since DAI is over-collateralized, it works in a way that reduces the risk of Ethereum price fluctuations, which means that the value of Ethereum backing DAI remains the same. Furthermore, DAI is a smart contract built on the Ethereum blockchain, making it a fully decentralized stablecoin that cannot be shut down by third parties.
Lending platforms
Decentralized lending platforms are also built on the Ethereum blockchain and allow users to lend and borrow currency without relying on intermediaries. Such products are available to anyone anywhere – all a person needs to do is own an Ethereum wallet.
At present, decentralized lending platforms use collateralized borrowing as a type of lending. This works by requiring borrowers to put up a larger collateral value than they borrow, eliminating the risk for lenders of not being repaid if borrowers fail to repay the loan.
Some examples of decentralized lending platforms would be MakerDAO, Compound, and Dharma.
Prediction markets
Prediction markets are groups of people speculating on outcomes of events. In such a marketplace, one can simply buy or sell predictions or, more specifically, buy or sell shares. There are two types of shares – “YES” (so-called “long shares”) and “NO” (so-called “short shares”). “YES” shares offer payouts in case an event occurs, while “NO” shares reward people if an event does not happen.
The payouts depend entirely on how much the buyer is willing to buy and how much the seller is willing to accept. Prediction markets are usually compared to derivatives, that is, the value of derivatives is proportional to the probability of a particular outcome.
Like other DeFi applications, prediction markets are based on Ethereum smart contracts, which allow two parties to reach an agreement governed by the rules implemented in the smart contract code, rather than relying on a third party such as a lawyer. Conversely, third-party data providers, known as “oracles”, are used to provide real-world off-chain data to the blockchain. With the help of oracles, smart contracts know to whom the payout should be released.
Pros and Cons of DeFi
DeFi movement can be examined from several contradictory viewpoints. Next, we take a look at the benefits and risks that come along with the notion of decentralized finance.
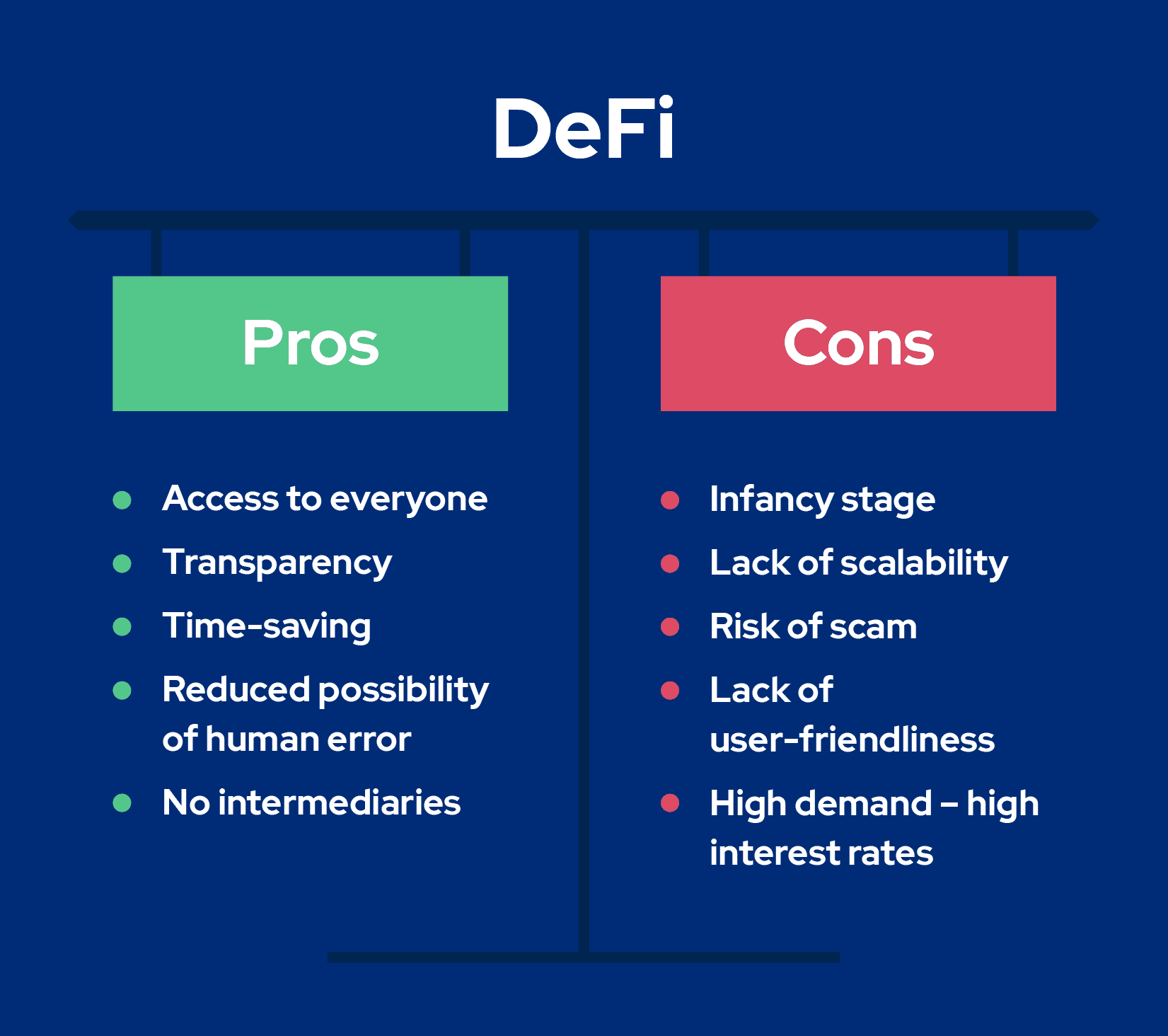
First, decentralized nature reduces the possibility of human error. Whereas mismanagement by central banks and their intermediaries could trigger a global crisis, smart contracts reduce such a risk unless they are written incorrectly.
Further, DeFi makes financial services accessible to nearly everyone. Instead of spending time going to the bank to take out a loan and relying on the bank to control your funds, one only needs a smart device and an internet connection to use financial services in need. Also worth mentioning is the elimination of waiting time for third party transaction approval.
After all, decentralized finance significantly increases the transparency of the financial ecosystem. All transaction details are recorded on the blockchain and therefore cannot be compromised in any way by central authorities.
Despite the benefits associated with DeFi, it is worth noting that the movement is still in its early stage. There are still many experiments and changes that may pose risks to DeFi. For example, mistakes made in Ethereum’s transition to PoW would lead to dangers for decentralized finance.
In addition, DeFi projects lack scalability. While centralized parties are able to process thousands of transactions per second, Ethereum can process about thirteen. As a result, it can take some time for transactions to be confirmed, plus they can become very expensive at congestion times.
What is more, even though DeFi promotes the idea of decentralization, not all DeFi services are fully decentralized, which means the risk of scam remains. As an example, InstaDapp wallet does not possess its own tokens, thus, users have no direct control over its development.
Finally, we can compare some of the DeFi features to centralized services like SpectroCoin. For instance, DeFi projects do not have their customer support to assist users on any issues or queries that arise while using their services.
DeFi applications tend to lack user-friendliness, leading to many questions which are crucial to the successful use of these platforms. Meanwhile, at SpectroCoin, not only do we offer a user-friendly interface but also a 24/7 live support in any language our customers need. This way, users can just drop any question and have all their queries answered in seconds.
When it comes to lending, DeFi project interest rates are based on demand and can be a lot higher than the industry average. Contrarily, the SpectroCoin Loans platform provides a crypto-backed lending solution with competitive loan rates and applies no hidden fees, no matter the demand.
Final thoughts
DeFi shines the light on financial services that are accessible to everyone. At the same time, it is attracting the attention of more and more participants in the crypto space who believe that the DeFi movement will one day become a full-fledged alternative to centralized finance.
However, there is still much to be done in the development of DeFi, such as fixing existing Ethereum issues and improving security and scalability. While we see it as an exciting movement, we believe the essence of decentralized finance is yet to be developed.
What are your thoughts on DeFi? Share your insights on our social media channels, we are thrilled to hear them!